Dbs101_flippedclass4
Topic: Advanced Aggregation Functions
Let’s get started
The flipped class was conducted on Advanced Aggregation Functions. We were divided into 4 groups and each group was assigned to a topic for presenting it to the class. Group 1 was to present on ranking, group 2 windowing, group 3 and 4 on pivoting and, rollup and cube respectively. We were given 30 minutes for discussing within the group and 20 minutes to present it to the class. For the presentation, we were expected to present the demo of the advanced aggregation function given to the group.
Expected Outcomes of this flipped class
- Implement advanced aggregation functions.
- Understand the need for advanced aggregation functions.
Ranking
Ranking functions are aggregate functions that assign a rank to each row in a result set based on specified criteria.
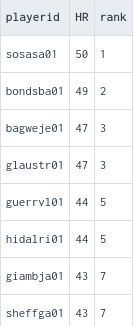
RANK: Assigns a rank to each row based on the ordering criteria. Rows with the same values in the ordering columns receive the same rank, and the next rank is skipped.
DENSE_RANK: Similar to RANK, but it does not skip ranks when there are ties. If multiple rows have the same values in the ordering columns, they are assigned consecutive ranks without gaps. 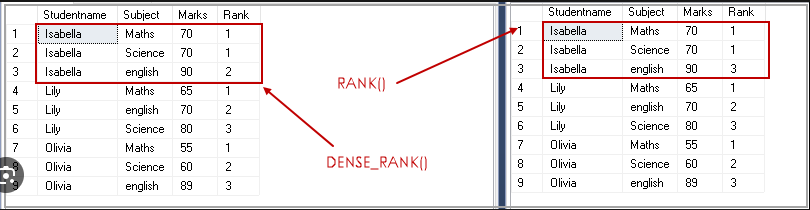
Windowing
Window frame designates a subset of consecutive rows adjacent to the current row in the window that will be evaluated as a group. There are three parts in a windowed aggregation:
PARTITION BY- indicates how the query results are divided into groups.ORDER BY- determines in what order the aggregations will be applied.ROWS BETWEENor RANGE BETWEEN- ROWS BETWEEN specifies the distance in number of rows and RANGE BETWEEN specifies the distance in the values.
Some examples of common uses of windowed functions:
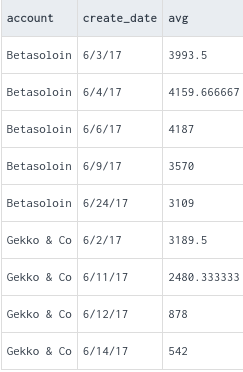
AVG OVER: Calculates the average value of a specified column over a window defined by the ORDER BY clause.
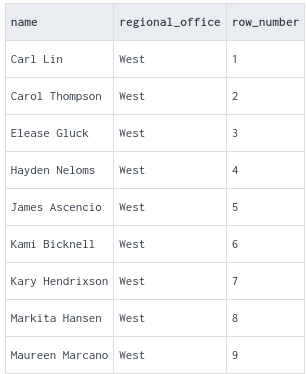
ROW_NUMBER: Assigns a unique sequential integer to each row in the result set, starting from 1.
RANK: Assigns a rank to each row based on the ordering criteria specified in the ORDER BY clause.
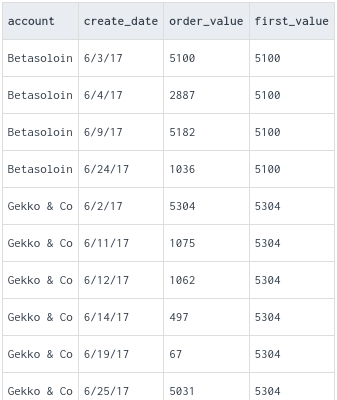
FIRST_VALUE: Returns the value of a specified expression (typically a column) from the first row in the window frame.
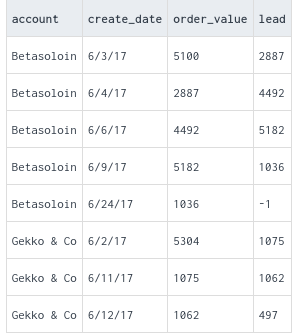
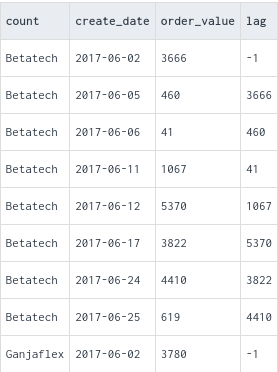
LEAD: Returns the value of a specified expression from the next row in the result set, relative to the current row.
LAG: Returns the value of a specified expression from the previous row in the result set, relative to the current row.
Pivot
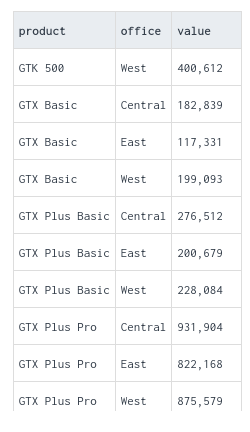
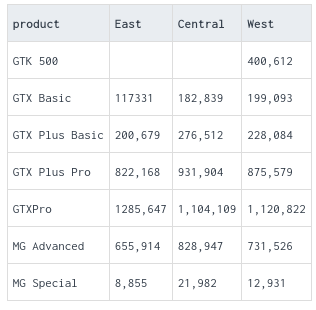
PIVOT enables you to see rows as columns in a query result.Pivot tables are a powerful tool for data analysis and visualization, offering flexibility and ease of use for exploring and summarizing datasets in various ways.
before pivoting
after pivoting
1
PIVOT can’t be used with WHERE, GROUP BY, or HAVING after the PIVOT clause.
Rollup and cube
ROLLUP generates multiple levels of subtotals based on the hierarchy of columns specified in the GROUP BY clause and rollup is commonly used in financial reporting, sales analysis, and other scenarios where hierarchical summaries are needed.
CUBE generates all possible combinations of values from the specified columns in the GROUP BY clause, producing comprehensive summary data and it is particularly useful when you want to analyze data from multiple dimensions simultaneously.
Experience
Today’s flipped class topics were easy and interesting and all the 4 groups did try their best in presenting it to the class with the demo of the aggregate function given to the group. It was actually interesting class so I would rate it 5 on 5..